
Data from an interim analysis of an ongoing phase II study suggest that patients with carcinoid and pituitary NETs, who have been traditionally chemo-resistant, may obtain "extraordinary responses" with capecitabine and temozolomide.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Data from an interim analysis of an ongoing phase II study suggest that patients with carcinoid and pituitary NETs, who have been traditionally chemo-resistant, may obtain "extraordinary responses" with capecitabine and temozolomide.

Single-agent neoadjuvant capecitabine combined with radiation therapy demonstrated similar outcomes as previously established standards of care for patients with stage II or stage III rectal cancer.

The combination of ramucirumab and paclitaxel resulted in a significant prolongation in survival and gains in quality of life when compared to paclitaxel alone for the second-line treatment of patients with metastatic gastric cancer.

Combining two specific anti-cancer vaccines, rather than administering one as monotherapy, doubles the 1-year survival probability in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), according to the results of a phase II study presented January 14.

An analysis of phase III, second-line data has shown that RAS mutations beyond KRAS exon 2 are negative predictive biomarkers for the EGFR-inhibitor panitumumab in metastatic colorectal cancer.
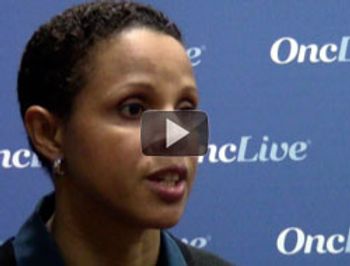
Elizabeth Garner, MD, MPH, vice president, Clinical Affairs, Preventive Care, Myriad Genetics, discusses the myRisk Hereditary Cancer Test.

Postneoadjuvant bisphosphonate therapy in women with residual invasive disease following chemotherapy for primary breast cancer does not improve clinical outcomes, according to an interim analysis of a large phase III clinical trial presented at the 2013 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.

Laura J. Esserman, MD, discusses the I-SPY 2 trial, a clinical trial for women with newly diagnosed, locally advanced breast cancer.

Andrew J. Brenner, MD, PhD, from the Cancer Therapy Research Center, discusses the link between obesity and breast cancer outcomes.
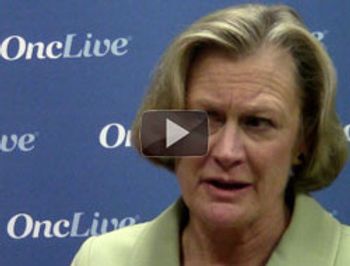
Julie R. Gralow, MD, from the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, discusses the SWOG S0500 trial, which evaluated different therapies for patients with metastatic breast cancer who had elevated circulating tumor cell levels.

The first results from the novel the I-SPY 2 trial show encouraging possibilities for a veliparib/carboplatin combination therapy in TNBC.

Antiangiogenic therapy with ramucirumab, an investigational agent that binds to VEGFR-2, added to first-line docetaxel failed to delay the progression of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.

Switching chemotherapy based on level of elevated circulating tumor cells after one cycle of chemotherapy did not improve OS or PFS in women with metastatic breast cancer.

The addition of carboplatin to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy increased pathologic complete response rates in patients with triple-negative breast cancer.

Combination treatment with idelalisib plus rituximab was associated with a >70% improvement in OS in patients with high-risk relapsed/refractory CLL.

The combination of everolimus, trastuzumab, and vinorelbine, as given in the BOLERO-3 trial in patients with pretreated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer, is adequately tolerated, and adverse events are manageable.

Kristi McIntyre, MD, from Texas Oncology, discusses the results of a phase II, multicenter, single-arm study that studies eribulin mesylate as first-line therapy for locally recurrent or metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer.
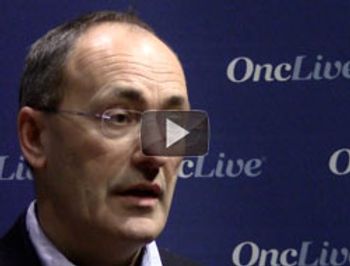
Matthew J. Ellis, MD, PhD, from the Siteman Cancer Center, discusses the ongoing phase III FALCON trial.
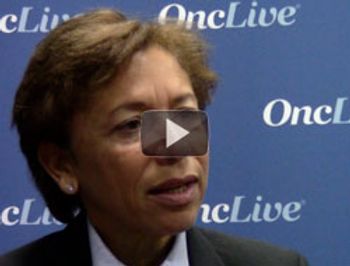
Edith A. Perez, MD, professor of medicine, Mayo Clinic, discusses the antibody drug conjugate T-DM1 as a treatment for patients with breast cancer.

In women with metastatic breast cancer that responds to frontline chemotherapy, locoregional treatment (LRT) of the primary tumor and axillary nodes does not produce an increase in overall survival (OS),

PIK3CA-mutated tumors in patients with HER2-positive (HER+) breast cancer (BC) are associated with a much lower rate of pathological complete response (pCR). The lowest pCR was observed in HER2+/hormone receptor-positive (HR+), PIK3CA-mutated tumors.

Adam Brufsky, MD, PhD, FACP, discusses the tnAcity trial, which is aimed to clarify how best to use existing drugs in patients with triple-negative breast cancer.

Almost half of patients with relapsed/refractory AML had complete remissions when treated with quizartinib, which also had a more favorable safety profile as compared with higher doses.

A prescribed exercise program reduces joint pain in breast cancer survivors taking AIs, with pain reductions observed at all levels of exercise.

Anastrozole may be a new option for primary prevention of breast cancer in postmenopausal women at high risk for the disease.

Andre Goy, MD, MS, from the John Theurer Cancer Center, discusses the apparent effectiveness of CD19-targeted CAR-modified T cells as a treatment for patients with various types of lymphoma.

Pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy had a significant correlation with survival in early HER2-positive breast cancer after 4 years of follow-up.

Bevacizumab did not improve invasive disease-free survival or overall survival when added to adjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer in the large randomized BETH trial.

Brentuximab vedotin has demonstrated antitumor activity in the setting of relapsed or refractory DLBCL across a broad range of CD30 expression, including low or undetectable CD30 expression.

Adding the tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib to standard aromatase inhibitor therapy with letrozole doubled PFS compared with letrozole alone in women with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.