
Although lung cancer still causes more deaths than any other type of malignancy not only in the United States but throughout the world, there’s a sense of excitement in the air these days when it comes to helping people with this disease.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Although lung cancer still causes more deaths than any other type of malignancy not only in the United States but throughout the world, there’s a sense of excitement in the air these days when it comes to helping people with this disease.

Significant progress has been made in recent years in understanding the biology and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors.
The growing incidence of primary liver cancer in the United States poses a great therapeutic challenge.

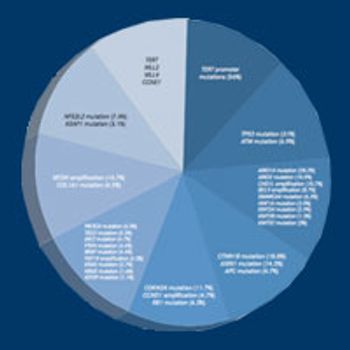
Gastroesophageal cancer (GEC) is a complex disease, encompassing cancers with different histological and molecular subtypes. Growing insight into the molecular biology of GEC is poised to change the treatment landscape for this disease, although many questions remain unanswered.

Tepotinib, an investigational small molecule that targets a recently identified aberration in the MET gene, is moving forward rapidly in clinical development for patients with non–small cell lung cancer who harbor the mutation, raising hopes that a more specific attack on the signaling pathway will lead to a new therapy for a significant subgroup of individuals with the disease.

It was not that long ago that decisions regarding cancer management were essentially made exclusively by the treating physician, with patients simply being informed of “the plan” for their treatment.