Head & Neck Cancers
Latest News
Video Series

Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

Treatment of head and neck cancer often leaves patients with aftereffects that are bothersome at the very least and life-altering at their worst.
Minimally invasive transoral robotic surgery, used alone or combined with adjuvant therapy, provides good functional and oncologic outcomes in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.

A retrospective analysis of the risks of hypothyroidism in patients who received sunitinib and sorafenib is gaining attention in the field of head and neck cancers.

The Trials in Progress section supplies summaries of ongoing research in a broad range of cancer types.
Patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma who had matted lymph nodes -- nodes that are connected together -- are more likely to metastasize than those without matted lymph nodes.

Approximately 7% of Americans are infected with oral human papillomavirus (HPV), and men are 3 times as likely to be infected as women.

Acupuncture may help prevent xerostomia in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy and may also reduce symptom severity.

Researchers are dissecting new studies regarding targeted therapies as well as combined therapeutic approaches for HPV in the progression of head and neck cancers.

Researchers are reporting favorable early results with the addition of bevacizumab to conventional chemoradiation in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer.
Human papillomavirus is perhaps best known as the main cause of cervical cancer, but if recent trends continue, by 2020 HPV will cause more cases of oropharyngeal cancer each year than cervical cancer.

Radiotherapy often results in the loss of some salivary gland function, causing hyposalivation and xerostomia.
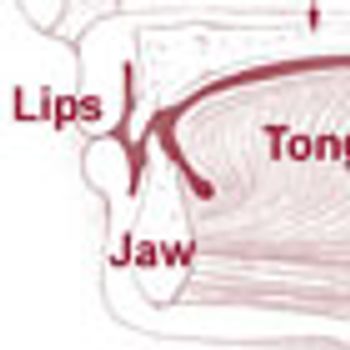
Approximately 7% of Americans carry the human papillomavirus (HPV) in their oral cavities, and men are 3 times more likely to carry the virus than women.

In an era when advances in chemoradiation and targeted therapies have revolutionized treatment in head and neck oncology patients, it's possible that treating physicians might not know where surgery fits into the regimen.

Chemotherapy given at the same time as radiotherapy may be a feasible treatment for high-risk nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) of the head and neck.
The investigational compound cabozantinib (formerly known as XL184) has generated much excitement in recent years for its ability to target multiple pathways involved in the development of cancer.

Some cosmetologists and barbers inspect their customers' scalps, necks, and faces for the presence of skin lesions that they think may be cancerous.

As the incidence of head and neck cancers linked to the HPV continues to rise, a federal advisory panel has recommended that all 11- and 12-year-old boys be vaccinated against the virus.

Ezra E. W. Cohen, MD, has focused on the role of EGFR inhibitors in much of his research into head and neck cancers.

Dr. Ezra Cohen from the University of Chicago Discusses Head and Neck Cancer Pathways

If IKK kinase, a group of inhibitory proteins, activity is not regulated properly, tumors in the body have the ability to migrate and proliferate.

Ezra E. W. Cohen, MD, is a physician and translational researcher at the University of Chicago Medical Center, that focuses on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors.
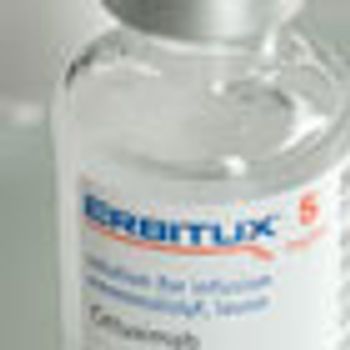
Cetuximab (Erbitux) was approved by the FDA for treating patients with late-stage head and neck cancer in combination with chemotherapy.

This month's collection of trials in progress highlights trials presented at the 2011 American Society of Clinical Meeting.

Dr. Barbara Burtness from Fox Chase Cancer Center on the Head and Neck Symposium Design

Dr. Barbara Burtness from Fox Chase Cancer Center Discusses the Upcoming Head and Neck Cancer Symposium