
Mosunetuzumab, a novel bispecific antibody, generated durable responses in patients with highly refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including complete remissions in 22.2% of those who had previously received chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Mosunetuzumab, a novel bispecific antibody, generated durable responses in patients with highly refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including complete remissions in 22.2% of those who had previously received chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting both BCMA and CD38 induced an objective response in >90% of patients with multiple myeloma who had been treated with at least 3 prior therapies and whose disease had spread outside of the bone marrow.

Acalabrutinib (Calquence) as a single agent or in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) significantly improved progression-free survival compared with obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in treatment-naïve patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

CC-93269 showed encouraging signs of dose-dependent efficacy with a safety profile that continues to be refined for patients with heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

An investigational new drug application for the therapy, which is labeled FT596, was approved in September 2019 and human trials are scheduled to begin in the first quarter of 2020.

Ahead of the 2019 ASH Annual Meeting, C. Ola Landgren, MD, PhD, shares insight on the potentially practice-changing data in the multiple myeloma paradigm that will be discussed at the conference.
Daniel A. Barocas, MD, MPH, FACS, an associate professor in the Department of Urology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, discusses the Comparative Effectiveness Analysis of Surgery and Radiation (CEASAR) trial in localized prostate cancer.

Kathryn E. Beckermann, MD, PhD, instructor of medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, discusses sequencing strategies in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).

A triplet combining the PD-1 inhibitor spartalizumab with dabrafenib and trametinib led to a 12-month overall survival rate of 86.1% for patients with previously untreated advanced BRAF V600–mutant melanoma.

Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, discusses the rationale for BRAF/MEK combinations and immunotherapeutic combinations in melanoma and ongoing research examining triplet regimens.

Georgina V. Long, BSc, PhD, MBBS, FRACP, discusses the findings from a subgroup analyses of the CheckMate-067 trial.

Eric Shinohara, MD, MSCI, discusses the emergence of stereotactic body radiotherapy to treat patients with prostate cancer.

The combination of cobimetinib (Cotellic) and vemurafenib (Zelboraf) maintained an advantage for overall survival and objective response rate in patients with BRAF-positive melanoma versus vemurafenib alone.

Patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600-mutant melanoma who achieve a complete response to dabrafenib (Tafinlar) plus trametinib (Mekinist) are more likely to have improved survival outcomes at 5 years.
Isabella C. Glitza, MD, discusses a single-center phase I/Ib trial of concurrent intravenous and intrathecal nivolumab for patients with metastatic melanoma and leptomeningeal disease.
Grant McArthur, PhD, discusses significant results from the final analysis of the coBRIM trial, which evaluated the 5-year survival data of cobimetinib plus vemurafenib in patients with BRAF V600-mutated advanced melanoma.

Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC; Imlygic) prior to surgery was associated with improved recurrence-free survival and overall survival compared with surgery alone in patients with resectable advanced melanoma.

Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, discusses the significance of the BRAF/MEK combination dabrafenib and trametinib, which was the first BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimen to be approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with BRAF V600E–positive stage III melanoma following complete resection.

Adil Daud, MD, discusses the role of dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma and highlighted other combinations under investigation.

The combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy) showed a sustained survival benefit compared with nivolumab or ipilimumab alone, according to 5-year follow-up results.
Gaudenz Danuser, PhD, discusses how the activation of RacP29S impacts the treatment of patients with melanoma. His lab has been studying the Rac molecule for around 20 years. The RacP29S mutation most commonly appears in melanoma, but it has since been discovered in a few other cancer types as well.
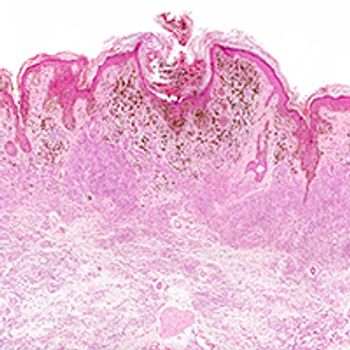
Combining a BRAF inhibitor with a MEK inhibitor causes endoplasmic reticulum stress in BRAF wild-type, NRAS­-mutated melanoma cells, resulting in significant antitumor activity.
David F. Penson, MD, MPH, MMHC, discusses treatment selection in patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer.
Allison Betof Warner, MD, PhD, discusses the excitement surrounding the findings from the COMBI-i trial that was presented at the 2019 ASCO Annual Meeting. This trial investigated the combination of PD-1 inhibitor spartalizumab with dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with advanced BRAF V6000mutant melanoma.

Alexander N. Shoushtari, MD, discusses the significance of the findings from the first-in-human trial evaluating tebentafusp, a TCR–CD3 bispecific, in patients with advanced melanoma.

Sam S. Chang, MD, MBA, discusses the shift toward personalized therapy in prostate cancer.

David Morris, MD, FACS, provides an update on the 3 newest agents available for nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treatment and discussed factors to consider when choosing among them.

Taofeek K. Owonikoko, MD, PhD, discusses current standard of care treatments for patients with small cell lung cancer.

Karen Kelly, MD, discusses how to determine treatment after patients with lung cancer progress on TKIs.

Suresh S. Ramalingam, MD, FASCO, highlights current and emerging therapies for 6 key actionable driver mutations in non–small cell lung cancer.