Lung Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use has granted a positive opinion for use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) as a treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic PD-L1-positive non–small cell lung cancer.

Patients with nonfunctioning neuroendocrine tumors of lung or gastrointestinal origin continued to live longer when treated with the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus (Afinitor) than with placebo.

Rolling submission of a new drug application for brigatinib (AP26113) has been initiated for patients with advanced ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer who are resistant to prior crizotinib (Xalkori).

Mark G. Kris, MD, medical oncologist, William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, explains what community oncologists need to know regarding immunotherapy and frontline treatment options for patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

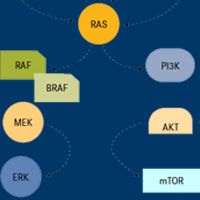
MET exon 14 skipping mutations are emerging as a particularly promising biomarker, at least in the context of lung cancer.

Frontline pembrolizumab (Keytruda) improved overall survival versus chemotherapy in non–small cell lung cancer patients with high levels of PD-L1 expression.

David Planchard, MD, PhD, Department of Medical Oncology, Thoracic Unit, Institut Gustave Roussy, discusses a phase II trial examining the combination of dabrafenib and trametinib in pretreated patients with BRAF V600E-mutant advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Phase I findings of a study examining the efficacy of osimertinib (Tagrisso) in heavily pretreated patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer and leptomeningeal disease showed promising activity in the patient population.

Hossein Borghaei, DO, discusses the significance of the 2-year follow-up results of the CheckMate-057 and -017 studies, the evolving role of PD-L1 as a biomarker and others that are in development, and emerging immunotherapy agents in the field of non-small cell lung cancer.
Melissa Johnson, MD, associate director, Lung Cancer Research, Sarah Cannon Research Institute, discusses the phase II BIRCH study, which is examining atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in patients with PD-L1–positive locally advanced or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

The European Commission approved bevacizumab in combination with erlotinib as a frontline treatment for patients with unresectable advanced, metastatic, or recurrent EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung cancer.

Alectinib improved progression-free survival by 66% compared with the current standard crizotinib as initial inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced or recurrent ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer.

Avelumab demonstrated clinical activity in patients with advanced or unresectable mesothelioma, with an overall response rate of 14.3%.

Patients with lung cancer who participated in a web-based system for reporting and tracking their symptoms achieved dramatic gains in survival compared with individuals who were followed with typical protocols.

The combination of dabrafenib and trametinib was highly effective as a treatment for patients with BRAF V600E-mutant non–small cell lung cancer.

Treatment with rovalpituzumab tesirine demonstrated single-agent activity and a manageable safety profile for patients with recurrent/refractory small cell lung cancer.

Upfront treatment with the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab demonstrated an objective response rate of 57% in patients with PD-L1-positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer.

Two-year follow-up data showed sustained improvements in overall survival with nivolumab in pretreated patients with either nonsquamous or squamous non–small cell lung cancer in updated findings from the phase III CheckMate-057 and -017 trials.

Treatment with the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab demonstrated a median overall survival of 7.7 months and a 1-year OS rate of 43% for patients with recurrent small cell lung cancer.
Hossein Borghaei, DO, chief, Thoracic Oncology, director, Lung Cancer Risk Assessment, associate professor, Department of Hematology/Oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, discusses 2-year follow-up results of the CheckMate-017 and -057 studies, which compared the efficacy of nivolumab (Opdivo) versus docetaxel in patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

The European Commission has approved everolimus (Afinitor) for use as treatment for patients with progressive, unresectable or metastatic, well-differentiated nonfunctional gastrointestinal or lung neuroendocrine tumors.

The FDA has approved new diagnostic tests for the detection of somatostatin receptor-positive neuroendocrine tumors and for EGFR mutations from blood samples for patients with non–small cell lung cancer.
Keith Kerr, BSc, MB, ChB, FRCPath, FRCPE, of the University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, Scotland, discusses PD-L1 immunohistochemistry in lung cancer.
The use of immunohistochemistry could be a more cost- and time-efficient first-line screening method for identifying ROS1 gene rearrangements to predict eligibility for crizotinib (Xalkori) for patients with non–small cell lung cancer compared with fluorescence in-situ hybridization.

Thierry M. Jahan, MD, discusses a study looking at the investigational cancer vaccine CRS-207 and its potential in mesothelioma.