
OncLive is pleased to announce that the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) has joined the OncLive Strategic Alliance Partnership program, a collaborative effort to bring up-to-date clinical information to practicing oncology specialists.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


OncLive is pleased to announce that the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) has joined the OncLive Strategic Alliance Partnership program, a collaborative effort to bring up-to-date clinical information to practicing oncology specialists.

Patients with head and neck cancer whose disease is associated with KRAS variant had significantly better progression-free survival and overall survival when treated with the monoclonal antibody cetuximab, according to findings of a retrospective analysis of a randomized trial.

Historically, patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma have had few treatment options, but several targeted agents and one immunotherapy, the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab, have been approved within the past 5 years, considerably expanding the RCC treatment arsenal. In the frontline setting, targeted agents are often the go-to therapy.

Patients with low-risk meningioma had a 3-year progression-free survival that modestly exceeded expectations after gross total resection followed by observation.

Patients with endometrial and cervical cancer reported significantly less acute gastrointestinal toxicity when treated with pelvic intensity-modulated radiation therapy as opposed to standard pelvic radiation therapy.

Chemoradiation for early-stage, low-grade follicular lymphoma led to significant improvement in progression-free survival compared with involved-field radiotherapy alone.

The moonshot was one of many topics discussed at a September 14 policy briefing held by the Ruesch Center for the Cure of Gastrointestinal Cancers at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center. Participants also discussed the growing cost of cancer research and the implications for policy makers, health care professionals, patients and society.

Improved understanding of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia and expanded treatment options have made individualized treatment based on clinical indications a feasible strategy

Despite multiple therapeutic advances in recent years, proteasome inhibitors remain a cornerstone of therapy for multiple myeloma, both newly diagnosed and relapsed and refractory disease.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells offer highly effective therapy for patients with minimal residual disease or bulky disease in both aggressive and indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas.

Recent success with novel agents for chronic lymphocytic leukemia has spurred development of more agents in the same therapeutic classes; however, definitive advantages over the originals have yet to be established.

Almost 90% of patients with previously treated light chain amyloidosis responded to single-agent daratumumab (Darzalex).

Combining the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax (Venclexta) with the anti-CD20 agent rituximab (Rituxan) led to objective responses in 86% of patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

The Wistar Institute, an international leader in cancer, immunology and infectious diseases research, is pleased to announce that Ashani Weeraratna, PhD, associate professor and program leader in the Tumor Microenvironment and Metastasis Program, has been named the Ira Brind Associate Professor.

Currently available therapies offer meaningful clinical benefits to patients with myelofibrosis, but achieving remission will likely require new molecules targeting different pathways.

Diagnostic criteria and therapeutic strategies for myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative neoplasms continue to evolve as molecular and genetic studies have provided new insights into the diseases.

Clinical experience with lenalidomide (Revlimid) in myelodysplastic syndromes has provided evidence of potential to improve survival and reduce the leukemic progression in patients with 5q-deletion.

An international leader in harnessing a patient's own stem cells to fight cancer and autoimmune diseases joined the faculty of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center on September 1.

John D. Minna, MD, who helped establish the first tumor lines and discover the c-Myc oncogene in lung cancer, was honored in the Lung Cancer category with a 2015 Giants of Cancer Care award, a program that OncLive launched to recognize leaders in the field.

Adam Bass, MD, discusses the various subclasses of gastric and esophageal cancer, mechanisms by which cancers are activated within a patient from dormancy, and the potential for uncovering an optimal treatment regimen for individual patients.

After a decade of advances in the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer, researchers are looking for ways to improve outcomes through a more personalized approach that includes risk-based strategies and appropriate use of molecular testing.

Mario Dicato, MD, Hematology-Oncology Service, Centre Hospitalier de Luxembourg, discusses 3 agents used for the treatment or reduction of thrombocytopenia for patients with cancer.

David H. Ilson, MD, PhD, medical oncologist, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, discusses how the treatment paradigm of gastric cancers will evolve in the future.
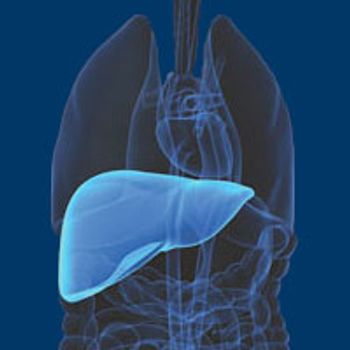
Topline results from the phase III RESORCE trial demonstrated that second-line treatment with regorafenib (Stivarga) represented a 38% reduction in the risk of death compared with best supportive care in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.

Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, whose work has helped guide and define the growing array of anticancer immunotherapy drugs, was honored in the Melanoma category with a 2015 Giants of Cancer Care® award, a program that the Intellisphere® Oncology Specialty Group launched to honor leaders in the field.

Geoffrey R. Oxnard, MD, discusses the potential for BRAF-targeting therapies in non-small cell lung cancer.

Experts identify practice-changing or noteworthy abstracts in their field from the research presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting.

Even as our understanding of the biology of prostate and bladder cancers improves and treatment protocols are refined, there remain many clinical scenarios in which no clear-cut answers are available.

Potential to render cancer cells less able to cope with hypoxia.

Outstanding individuals across all specialties of oncology were recognized at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting with the organization’s highest honors, the 2016 Special Awards.