
Melinda L. Telli, MD, is actively involved in clinical research that focuses on DNA repair targeted therapeutics for the treatment of triple-negative and BRCA1/2 mutation-associated breast cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Melinda L. Telli, MD, is actively involved in clinical research that focuses on DNA repair targeted therapeutics for the treatment of triple-negative and BRCA1/2 mutation-associated breast cancer.
In spite of the setbacks, researchers remain hopeful that a better understanding of the mechanism of action for PARP inhibitors will lead to effective treatment of a wide variety of cancers.
Antibodies directed against tumor cell antigens or overexpressed proteins are currently the fastest-growing class of targeted cancer therapeutics.

Leonard M. Neckers, PhD, has been studying the role of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 in signal transduction and the translational development of Hsp90-targeted anticancer agents for two decades.
Hsp90 may be referred to as the 'guardian of the proteome,' since it regulates the correct structure and function of many of the important proteins encoded by our DNA.
The MET signaling network has emerged as an important target for cancer therapy, with a particularly significant role in controlling the cancer hallmarks of metastasis and angiogenesis.

Jill M. Siegfried, PhD, is an investigator into the role of growth factors and hormones in the development and growth of lung cancer.

Since the discovery of the HER2/neu gene in the late 1970s, aberrations in the HER2 signaling pathway have been implicated in a wide variety of human cancers.
Dennis Slamon, MD, PhD, and Carlos L. Arteaga, MD, discuss recent advances in anti-HER2 targeted therapies and the role of signaling by oncogenes.
Hanahan and Weinberg initially outlined 6 hallmarks that they believed were essential to the transformation of normal cells into malignant cancer cells in most, if not all, human cancers.

Dr. Yuri Lazebnik's research focuses on how cells become cancerous, how cancer cells evolve, and how they can be killed selectively.

As its moniker As its moniker "guardian of the genome" suggests, p53 has become recognized as one of the most important cancer-related molecules in the cell.
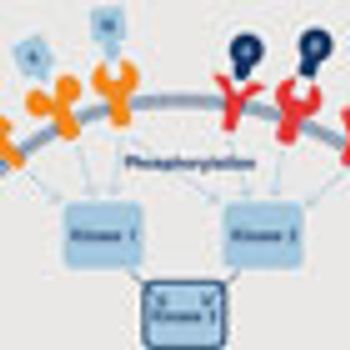
Since its discovery, phosphorylation has come to be recognized as a global regulator of cellular activity, and abnormal phosphorylation is implicated in a host of human diseases.

Martin Steffen, MD, PhD, developed phosphorylation signatures that discriminate between lung tumors and normal lung, and is developing signatures for the prediction of therapy response.
This year marks more than 20 years of research into the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway.

Josep Tabernero, MD, is actively involved in clinical research with molecular targeted therapies, with a focus on EGFR-family and PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway inhibitors, in phase II and III studies with new chemotherapy agents in gastrointestinal tumors.
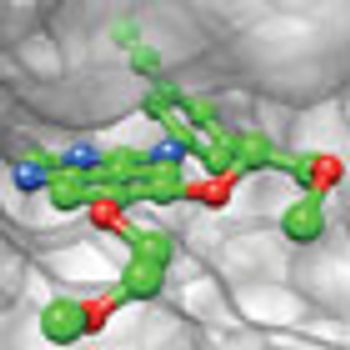
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is the prototypical receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) and one of the most comprehensively studied molecular targets in clinical oncology.
The breadth of the stem cell factor (SCF)/ KIT signaling pathway oncogenic functions and potential role as a therapeutic target are just now becoming clear.
Intense research has resulted in JAK-STAT becoming one of the best-understood signal transduction cascades.

The first drug that successfully targeted the HER2 pathway in cancer treatment generated much excitement.
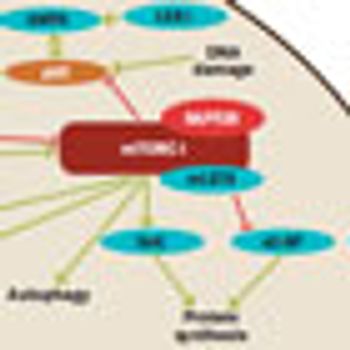
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a master switch, central regulator, or key integrator of cell growth and proliferation
The Hedgehog gene is an intracellular signaling ligand that initiates the Hh pathway, which is important in the regulation of embryo development from flies to humans