Immuno-Oncology
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The combination of atezolizumab, bevacizumab, carboplatin, and paclitaxel educed the risk of death by 22% compared with bevacizumab and chemotherapy in patients with advanced wild-type non-squamous non–small cell lung cancer.
Robert M. Jotte, MD, PhD, medical director and co-chair, USON Thoracic Committee, Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers, discusses the phase III findings of the IMpower131 trial, which looked at the addition of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) to frontline carboplatin and nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane) in patients with advanced squamous non
Mario Sznol, MD, professor of medicine, co-director, Yale SPORE in Skin Cancer, Yale Cancer Center, discusses immunotherapy combinations in renal cell carcinoma.

Two separate early-phase clinical trials exploring daratumumab in combination with either a PD-1 inhibitor for multiple myeloma or a PD-L1 inhibitor for non–small cell lung cancer were terminated following a planned interim analysis.

Durvalumab significantly improved overall survival versus placebo when used as a sequential treatment in patients with locally-advanced, unresectable non–small cell lung cancer who had not progressed following standard chemoradiotherapy, according to updated findings from the phase III PACIFIC trial.

IMCgp100, a novel immune-based treatment, demonstrated a 1-year survival rate of 73% for patients with heavily pretreated, which is nearly double the historical expectations for patients with the disease.

Novel combination regimens anchored by pembrolizumab (Keytruda), atezolizumab (Tecentriq), or nivolumab (Opdivo) are opening the door to new options and an opportunity to personalize therapy in non–small cell lung cancer.

The FDA has issued a drug safety notification warning against the use of frontline single-agent immune checkpoint inhibition for patients with PD-L1–low expressing platinum-eligible urothelial carcinoma.

In March, the President’s Cancer Panel issued a report acknowledging the financial toxicity associated with cancer care across the spectrum of treatments and suggesting potential remedies.

The quest continues to identify a predictive biomarker of response to more precisely treat patients with checkpoint inhibitors that, while markedly beneficial to some patients, are not without their own costs and associated immune-related adverse effects.

The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has developed its first set of recommendations to help clinicians manage toxicities in the recognition of the variety of immune-related adverse events that patients receiving checkpoint blockade immunotherapy may experience.

Sandip P. Patel, MD, medical oncologist, assistant professor of medicine, University of California, San Diego, discusses the impact of immunotherapy on the treatment of patients with non–small cell lung cancer.

Toni K. Choueiri, MD, discusses recent advancements and shares his insight on the future treatment landscape of patients with kidney cancer.

Arjun V. Balar, MD, assistant professor, Department of Medicine, director, Genitourinary Medical Oncology Program, NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center, discusses the impact of the combination of durvalumab (Imfinzi) plus tremelimumab in metastatic bladder cancer.

Combination therapy with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab and the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib failed to improve overall survival versus regorafenib in previously treated patients with locally advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer, according to topline findings from the phase III IMblaze370 study.

Xiao X. Wei, MD, MAS, discusses managing possible adverse events of different systemic therapies in kidney and bladder cancer.

Guru P. Sonpavde, MD, navigates through the treatment landscape of urothelial carcinoma.

The FDA has granted a priority review to a supplemental biologics license application for atezolizumab for use in combination with bevacizumab, carboplatin, and paclitaxel for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer.

A supplemental biologics license application has been submitted to the FDA for the use of pembrolizumab in combination with standard chemotherapy as a treatment for patients with metastatic squamous non–small cell lung cancer.
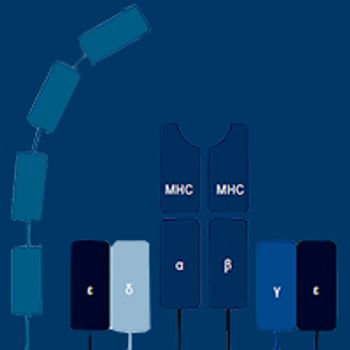
Components of the T-cell receptor complex, which links antigen recognition with T-cell activity and effector function, are being exploited for several types of cancer immunotherapy.

Edward B. Garon, MD, director of Thoracic Oncology at the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at University of California, Los Angeles, discusses immunotherapy combinations in non–small cell lung cancer.

The FDA has granted a priority review to a supplemental biologics license application for frontline pembrolizumab for use in combination with standard chemotherapy for patients with metastatic nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer.

Charles M. Rudin, MD, PhD, discusses ongoing developments with immunotherapy in patients with non–small cell lung cancer.

Dual immune checkpoint blockade with durvalumab (Imfinzi) and tremelimumab did not induce a statistically significant improvement in overall survival in heavily pretreated patients with locally-advanced or metastatic NSCLC.