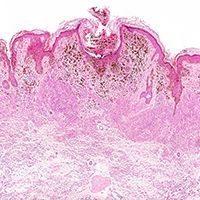
Melanoma & Skin Cancer
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Ryan Sullivan, MD, provides an overview of metastatic uveal melanoma, currently available treatment options, and unmet needs in the field.

Drs Babakoohi and Atlas share clinical pearls for community oncologists on treating basal cell carcinoma.

A look at how common metastatic basal cell carcinoma is in clinical practice and when to consider frontline immunotherapy.

Major pathological response and recurrence-free survival rates were improved in women vs men with melanoma who received BRAF/MEK inhibitor therapy in the neoadjuvant setting.

Real-world evidence is finding an expanded role in oncology, prompting experts to rethink how data are gathered on the day-to-day usefulness of drugs for regulatory decisions.

Experts review the safety and toxicity data of anti-PD-1 antibody agent cemiplimab for basal cell carcinoma treatment.

Ryan J. Sullivan, MD, discusses the examination of tebentafusp-tebn in uveal melanoma.

Shahab Babakoohi, MD, describes his monitoring strategies for patients with basal cell carcinoma.

Dr Jennifer Atlas leads a conversation on systemic therapy options in basal cell carcinoma with a review of clinical trial data.

Zeynep Eroglu, MD, discusses the rationale for investigating patterns of outcomes in patients with metastatic melanoma harboring BRAF mutations.
The European Commission has approved pembrolizumab for adjuvant treatment of adult and adolescent patients 12 years and older with stage IIB or IIC melanoma who have undergone a complete resection.

Hussein A. Tawbi, MD, PhD, discusses the safety profile of relatlimab plus nivolumab in patients with metastatic or unresectable melanoma, according to data from the phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial.

Treatment with the combination of cobolimab and dostarlimab led to an overall objective response rate and immune-related ORR of 42.9% consisting of all partial responses in patients with advanced or metastatic melanoma.

Experts review the currently available treatment options for locally advanced basal cell carcinoma.

Dr. Shahab Babakoohi explains when to refer a patient with basal cell carcinoma from a dermatology practice to a medical oncologist.

Adding talimogene laherparepvec to pembrolizumab led to encouraging responses with a manageable safety profile in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed on prior anti–PD-1 therapy, most notably in the adjuvant setting, according to findings from the phase 2 MASTERKEY-115 trial.
The PD-L1 antibody cosibelimab was found to elicit an encouraging objective response rate in patients with locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma who were not eligible to undergo curative surgery or radiation.

The combination of quavonlimab and pembrolizumab was found to be generally well tolerated and to have modest antitumor activity in patients with advanced melanoma that progressed on a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor, according to data from a phase 1/2 trial (NCT03179436).

Jennifer Atlas, MD, presents the clinical scenario of a man with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma.

Geoffrey T. Gibney, MD, discusses current treatment options for patients with melanoma, clinical trials that have explored different agents and combinations, and developing treatment options in uveal melanoma.

Shahab Babakoohi, MD, describes the incidence patterns, options for testing and diagnosis, and risk stratification for basal cell carcinoma.

Fixed-dose nivolumab plus relatlimab elicited continued progression-free survival benefit vs nivolumab alone in patients with treatment-naïve, unresectable or metastatic melanoma, according to updated results from the phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial.

Adjuvant pembrolizumab was found to result in a significant improvement in distant metastasis-free survival compared with placebo, with a continued reduction in risk of recurrence and an acceptable safety profile, in patients with resected stage IIB or stage IIC melanoma.

The FDA has lifted a partial clinical hold on the phase 1 NEON-2 trial investigating the use of davoceticept in combination with pembrolizumab in adult patients with advanced solid tumors or lymphoma.

The synthetic Toll-like receptor 9 agonist tilsotolimod reduced the sentinel lymph node biopsy positivity rate vs placebo in patients with localized, excised melanoma.