Melanoma & Skin Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Richard D. Carvajal, MD, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, describes the success of MEK inhibition in patients with advanced uveal melanoma using the agent selumetinib.

The FDA approved both dabrafenib and trametinib for the treatment of patients with metastatic or unresectable melanoma, as well as a companion diagnostic to properly identify the patients exhibiting the mutations that are targeted by these agents.

Arta Monjazeb, MD, and Michael Kent, DVM, from the UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center, describe an early phase trial exploring the potential of translating successful treatment from dogs to humans with advanced melanoma or sarcoma.

Combining the checkpoint antibodies ipilimumab and nivolumab led to deep tumor regression in approximately one-third of patients with advanced melanoma.

An antibody that targets PD-L1 to unleash the body's immune system has demonstrated a 21% response rate in a phase I study of patients with multiple solid tumors, setting the stage for an advance in immunotherapy with broad implications for treatment.

Lambrolizumab, an investigational antibody designed to target the programmed death-1 (PD-1) pathway in patients with melanoma, received a breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA after promising results from a small single-arm study.
Patients diagnosed with melanoma are typically affected psychologically. Researchers summarized health-related quality of life (HRQOL) during the 12-week ipilimumab induction period in previously treated patients diagnosed with advanced stage III or IV melanoma.

Analysis of the cost-effectiveness of ipilimumab compared with best supportive care in previously treated patients with advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma.
The novel immunotherapy talimogene laherparepvec has become the first oncolytic virus to successfully complete a phase III trial in advanced melanoma.

The FDA approved the radioactive diagnostic imaging agent technetium Tc 99m tilmanocept (Lymphoseek Injection) to identify lymph nodes for potential removal in patients with breast cancer or melanoma.

A new drug screening method revealed that cholesterol-reducing statin drugs used in combination with cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors might serve as an effective treatment approach for certain types of melanoma.

Circulating tumor cells can be a predictive blood biomarker for recurrence and survival in patients with stage III melanoma and may help identify who will benefit from aggressive adjuvant therapy.

Over the past decade, there has been an explosion of knowledge regarding the fundamental drivers of the malignant phenotype.

A phase III trial that compared nab-paclitaxel (nab-P; Abraxane) with dacarbazine (DTIC) in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma (MMM) found that nab-P nearly doubled the median time to progression-free survival (PFS).

Aleksandar Sekulic, MD, PhD, from the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ, discusses the administration of vismodegib for the treatment and prevention of basal-cell carcinoma in patients with basal-cell nevus syndrome.

Michael Rotkowitz, MD, from Cancer Treatment Centers of America, discusses a phase III trial that examined ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for patients with metastatic melanoma.

Jeffrey S. Weber, MD, PhD, specializes in cancer immunotherapy and has been involved in numerous trials of clinical drug development, vaccines, and studies on autoimmunity and melanoma.

Rajni Kannan discusses the importance patient education or managing the side effects associated ipilimumab and vemurafenib in metastatic melanoma.
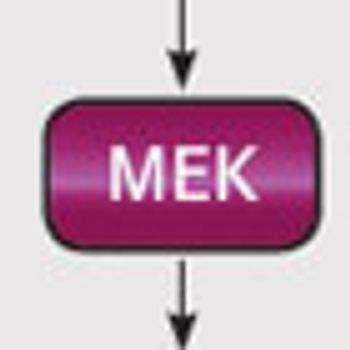
Though located far downstream of the extracellular trigger that initiates its signaling pathway, the MEK protein is no less significant a player in the cascade of events that promotes key cellular processes.

Antoni Ribas, MD, from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, discusses a phase I/II trial combining vemurafenib and ipilimumab for metastatic melanoma.
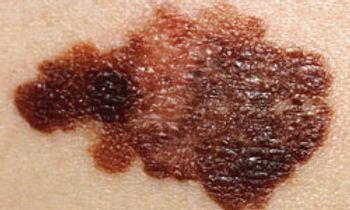
The incidence of melanoma, the deadliest of all skin cancers, is quickly rising, and the disease is responsible for more than 8000 deaths each year.

Nearly twice as many patients with metastatic melanoma who received a combination of ipilimumab and dacarbazine were alive after four years, suggesting that ipilimumab has long-term survival benefits.

Combining the new drugs dabrafenib and trametinib provided a clinically meaningful improvement in patients with melanoma that had BRAF V600 mutations.

Concurrent mutations in MEK1 and BRAF genes do not confer resistance to BRAF inhibitors in advanced melanoma, contrary to what investigators had expected.

The oral hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib is effective for both the prevention and treatment of basal-cell carcinoma in patients with the rare disorder known as basal-cell nevus syndrome.