
Adding daratumumab (Darzalex) to carfilzomib (Kyprolis) and dexamethasone reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 37% compared with carfilzomib and dexamethasone alone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Adding daratumumab (Darzalex) to carfilzomib (Kyprolis) and dexamethasone reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 37% compared with carfilzomib and dexamethasone alone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

Maintenance treatment with CC-486, an oral formulation of azacitidine, extended median overall survival by 9.9 months compared with placebo for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission.

Blinatumomab (Blincyto) as post-reinduction consolidation therapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation improved disease-free survival and overall survival by approximately 20% compared with intensive chemotherapy in pediatric and adolescent and young adult patients with high- or intermediate-risk of first relapse of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Enasidenib significantly improves complete remission and overall response when combined with azacitidine compared with azacitidine alone in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia with IDH2 mutations.

Treatment with the anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy KTE-X19 elicited a complete remission rate of 67% and an objective response rate of 93% for patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma.

Patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia had ongoing benefits 42 months after starting treatment with the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib.

CPI-0610 showed promising spleen volume responses and a meaningful reduction in total symptom score as monotherapy and in combination with ruxolitinib (Jakafi) for patients with refractory or intolerant advanced myelofibrosis.

Vecabrutinib, a reversible, noncovalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, exhibited evidence of clinical activity in adults with B-cell malignancies without producing any grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events.
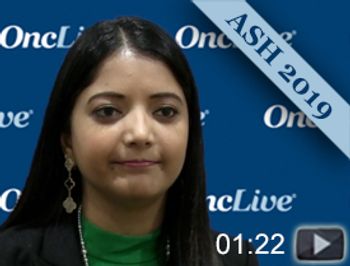
Deepu Madduri, MD, assistant professor, medicine, hematology and medical oncology, Mount Sinai Hospital, discusses the results of the phase Ib/II CARTITUDE-1 trial of the BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy JNJ-4528 in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
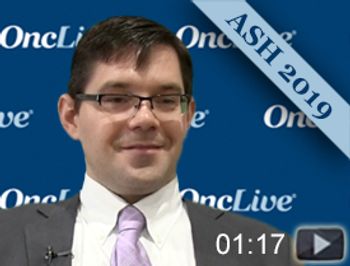
Benjamin L. Lampson, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, discusses preliminary safety and efficacy results from a phase II study of acalabrutinib (Calquence), venetoclax (Venclexta), and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).

The CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy lisocabtagene maraleucel showed promising clinical activity and manageable toxicity in heavily pretreated patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma, all of whom had progressed on ibrutinib.

Patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma who received a higher initial dose of duvelisib at 75 mg BID had a higher overall response rate of 62% than those who received 25 mg BID.

The BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib continues to demonstrate high overall response rates for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma, regardless of the presence of high-risk cytogenetics.

More than half of patients with heavily pretreated B-cell malignancies responded to the noncovalent BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, including those with resistance or intolerance to other BTK inhibitors or BCL2 inhibitors.

Steroid use while cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicities are at grade 1, instead of waiting until grade 3, reduces the rate of CAR T-cell treatment–related CRS and neurologic events.

The combination of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) elicited a 100% overall response rate in patients with relapsed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma that was refractory to rituximab (Rituxan).
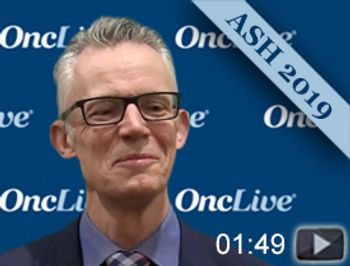
John F. Seymour, MBBS, PhD, clinical hematologist, associate director of Clinical Research, Peter MacCallum Centre, director of the integrated Haematology Department of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and the Royal Melbourne Hospital, discusses the 4-year update of the phase III MURANO trial in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).

Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, clinical director, Center for Lymphoma, Massachusetts General Hospital, discusses the pivotal safety and efficacy results from phase I TRANSCEND NHL 001 trial of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

The combination of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and rituximab showed a 34% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death compared with rituximab plus placebo in patients ≥70 years old with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, although it was not found to be statistically significant.

In patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma, treatment with ibrutinib might mitigate a historical trend toward decreased progression-free survival with succeeding lines of therapy.

CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy induced a high rate of rapid and durable complete responses in patients with aggressive relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

The triplet of umbralisib, ublituximab, and venetoclax induced a complete remission rate of 44% as a treatment for patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

The combination of polatuzumab-vedotin (Polivy), obinutuzumab (Gazyva), and lenalidomide (Revlimid) induced a high rate of durable responses in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma.

Constantine S. Tam, MD, MBBS, associate professor, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, discusses the results of the phase II CAPTIVATE study in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
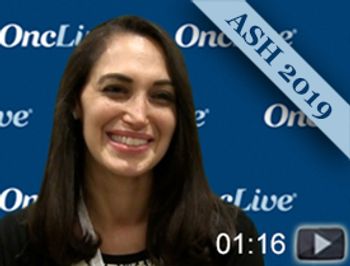
Noa Biran, MD, physician, John Theurer Cancer Center, discusses the 2-year update of a phase II trial of pembrolizumab (Keytruda), lenalidomide (Revlimid), and dexamethasone as post-autologous stem cell transplant consolidation in patients with high-risk multiple myeloma.

The triplet of acalabrutinib (Calquence), venetoclax (Venclexta), and obinutuzumab (Gazyva; AVO) is highly active as frontline therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

With extended follow-up, progression-free survival continues to be superior with the combination of ibrutinib and rituximab compared with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for patients ≤70 years with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

The first-line combination of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta) led to a 75% undetectable minimal residual disease rate in peripheral blood and 72% in bone marrow in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

The CAR T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel; Yescarta) induced a median overall survival of 25.8 months for patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

The BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy JNJ-4528 achieved a 100% overall response rate with early and deep responses in 29 patients with heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory myeloma.